Robot Vacuum Mapping, Sensors, and Navigation Explained
Robot vacuums are intended to make household cleaning easier by providing an automated option. Their efficiency is strongly dependent on improved mapping, sensor, and navigation technology. These methods enable robot vacuums to negotiate furniture, obstacles, and walls while providing comprehensive cleaning coverage. Mapping technologies assist the robot in determining the layout of a room, while sensors enable safe and successful navigation. Understanding how these elements interact allows you to appreciate how robot vacuums provide efficient, accurate, and hassle-free cleaning in homes of all sizes.

How Robot Vacuums Use Mapping for Efficient Cleaning?
Types of Mapping Technology: LiDAR, Camera, and Gyroscopes
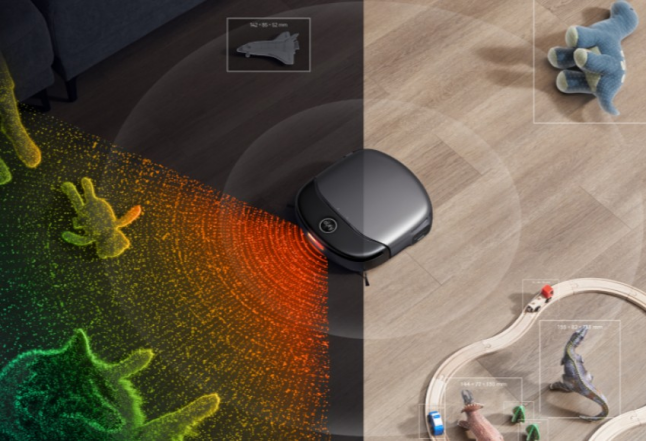
Robot vacuums employ a variety of mapping technologies to map out and navigate their surroundings. LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology scans and measures distances, resulting in a detailed map of the room. Cameras also assist the robot in navigating by recording visual data that allows it to avoid obstacles and map its surroundings. Gyroscopes, on the other hand, aid with balance and location by sensing rotation and direction. Each mapping method has capabilities, and many current robot vacuums combine these technologies to increase cleaning accuracy and efficiency.
Real-Time Mapping and Updating Cleaning Paths
Real-time mapping is an important characteristic of contemporary robot vacuums. As the vacuum goes around a space, it constantly examines the surroundings and changes its map to reflect any new impediments or spots that require attention. This dynamic technique enables the vacuum to change its cleaning course based on its surroundings, ensuring that no area is overlooked. For example, if a piece of furniture is moved, the vacuum will automatically readjust its route to suit the change. By continually updating its course, the robot ensures a more complete and effective cleaning operation, decreasing the need to repeat sections.
Advantages of Mapping for Coverage and Efficiency
Mapping significantly improves coverage and cleaning efficiency. With an exact map of the room, the robot vacuum can clean in a systematic and methodical manner, ensuring that all areas are covered. It prevents unnecessary cleaning, saving time and battery life. The vacuum can also identify which areas have already been cleaned, allowing it to concentrate on filthy regions. The vacuum achieves maximum coverage by essentially dividing the space into smaller, more manageable pieces. This capacity to design and execute cleaning pathways efficiently leads to a more effective and time-saving cleaning operation.

The Role of Sensors in Robot Vacuum Navigation
Obstacle and Cliff Sensors for Safe Navigation
Robot vacuums rely heavily on obstacle and cliff sensors to ensure their safety. Obstacle sensors detect physical things such as furniture, walls, and toys and keep the robot from colliding with them. When the vacuum encounters an obstruction, these sensors cause it to slow down or change course. Cliff sensors, on the other hand, detect drop-offs such as stairs or ledges and keep the vacuum from falling. These sensors work together to allow the robot to navigate the home securely, avoiding damage to itself and your furnishings while ensuring it does not tumble off edges or into dangerous places.
Anti-Collision Sensors and Bumper Technology
Anti-collision sensors and bumper technology combine to safeguard both the robot vacuum and your home's furniture. Anti-collision sensors identify impediments in the vacuum's route, allowing it to change its speed and direction to prevent an accident. When the vacuum makes contact with an item, the bumper, which is outfitted with sensors, absorbs the impact and triggers a reaction in the robot's navigation system. This guarantees that the vacuum does not become trapped or damaged. The combination of these technologies allows for more efficient navigation in small places and guarantees that your vacuum can continue to clean without causing damage to your furniture or itself.
Object Recognition and Avoidance Features
Object identification and avoidance are essential aspects of high-end robot vacuums. These systems employ powerful sensors and cameras to detect and categorize things in the robot's surroundings. The vacuum can then identify whether the object, such as a pet or a piece of furniture, should be avoided or cleaned around. Robot vacuums use machine learning and computer vision to continually improve their capacity to detect and respond to items, ensuring that they do not collide with or become entangled in obstructions. These characteristics improve efficiency by allowing the vacuum to clean continuously and lowering the danger of damage.
How Navigation Technology Enhances Cleaning Performance?
Smart Navigation vs. Random Path Navigation
Smart navigation and random route navigation are two important ways that influence how robot vacuums clean. Smart navigation uses smart mapping and sensors to develop efficient, methodical cleaning patterns that ensure complete coverage while minimizing overlap. This strategy allows the vacuum to proceed gradually from one region to the next, maximizing time and battery life. In contrast, random path navigation requires the vacuum to go in unpredictable ways, which might result in ineffective cleaning and missed places. While random navigation may still get the job done, smart navigation provides more precise, efficient, and effective cleaning results.
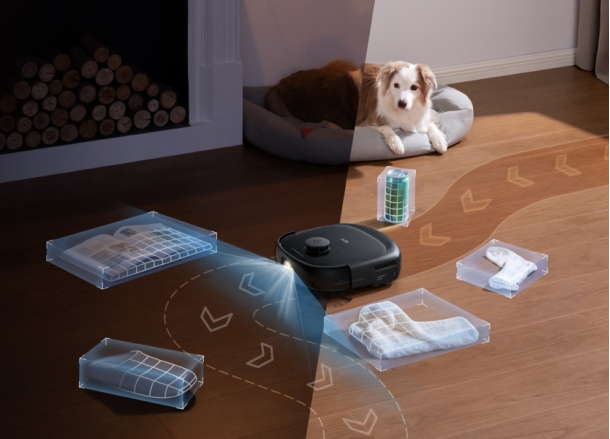
Zoning and No-Go Zones for Targeted Cleaning
Zoning and no-go zones are characteristics that improve the vacuum's ability to target specified regions while avoiding others. Zoning allows users to identify certain sections of the home where they wish the vacuum to concentrate its cleaning efforts, such as high-traffic areas or rooms with severe dirt buildup. No-go zones are regions where the robot is not supposed to go, such as around fragile goods or under low furniture. These capabilities provide consumers more control over the cleaning process, ensuring that the robot cleans the most important areas while avoiding spots that are inappropriate or off-limits.
Pathfinding Algorithms and Cleaning Efficiency
Pathfinding algorithms are critical to increasing the cleaning efficiency of robot vacuums. These algorithms determine the most efficient route for the vacuum to travel, ensuring that the whole area is covered without excessive retracing. They interact with the robot's mapping technology to alter the cleaning course as new barriers or environmental changes are recognized. Pathfinding algorithms speed up and improve the vacuum cleaning process by eliminating overlap and time spent on previously cleaned regions. This increased efficiency enables the vacuum to clean more spaces while using fewer batteries and completing the task faster.
Conclusion
Robot vacuums use advanced mapping, sensing, and navigation technology to clean efficiently and precisely. These vacuums use innovative mapping algorithms to build precise floor layouts, adjust to environmental changes, and ensure complete coverage. Sensors assist in ensuring safe movement around obstacles and prevent falls, while object identification improves overall productivity by minimizing unwanted disruptions. Robot vacuums can clean big spaces effectively and quickly thanks to clever navigation and pathfinding algorithms. When considering what to look for in robot vacuum models, understanding these technologies will help you choose the right vacuum that best fits your needs. As these technologies continue to improve, robot vacuums will become even more effective in providing high-quality cleaning results.